RSNA Press Release
- Researchers hope to reduce emergency C-section deliveries using MRI and a new "virtual childbirth" software application.
- The software uses 3-D reconstructed images of the mother's pelvis and the fetus with possible trajectories of the baby's head through the birth canal to determine the likelihood of a normal delivery.
- In the U.S., C-sections account for approximately one-third of all births.
Virtual Childbirth Simulator Improves Safety of High-Risk Deliveries
Released: November 29, 2011
| Media Contacts: | RSNA Newsroom | 1-312-949-3233 |
| Before 11/26/2011 or after 12/01/2011: | RSNA Media Relations: | 1-630- 590-7762 |
| |
Linda Brooks 1-630-590-7738 lbrooks@rsna.org |
Maureen Morley 1-630-590-7754 mmorley@rsna.org |
CHICAGO—Newly developed computer software combined with magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) of a fetus may help physicians better assess a womans potential for a difficult childbirth. Results of a study using the new software were presented today at the annual meeting of the Radiological Society of North America (RSNA).
Because a womans birth canal is curved and not much wider than a fetuss head, a baby must move through the canal in a specific sequence of maneuvers. A failure in the process, such as a head turned the wrong way at the wrong time, can result in dystocia, or difficult labor.
"The mechanics of the human birth canal make for a very complicated delivery process compared to other mammals," said Olivier Ami, M.D., Ph.D., an obstetrician in the Department of Radiology at Antoine Béclères Hospital, Université Paris Sud, France. "We now have computer-simulated childbirth to identify potential problems."
Using the new software, called PREDIBIRTH, Dr. Ami and a team of researchers processed MR images of 24 pregnant women. The result was a three-dimensional (3-D) reconstruction of both the pelvis and the fetus along with 72 possible trajectories of the babys head through the birth canal. Based on these simulations, the program scored each mothers likelihood of a normal birth.
"This goes beyond simple imaging," Dr. Ami said. "The software simulates the properties of potential deliveries."
For purposes of the study, the PREDIBIRTH scores were computed retrospectively and measured against delivery outcomes for the 24 women. Thirteen women delivered normally. These deliveries were scored as highly favorable by the simulator. Three women who delivered by elective cesarean-section (C-section)—two of which involved babies of excessive weight—were scored at high risk for dystocia.
Of the five women delivered by emergency C-section, two involved heart rhythm abnormalities and were scored mildly favorable and favorable. Three involved obstructed labor, all of whom scored at high risk of dystocia. Three women delivered with vacuum extraction and had mildly favorable simulator scores.
"The results in predicting dystocia were highly accurate," Dr. Ami said. "Our simulation predictions seem to be a significant improvement over pelvimetry."
Pelvimetry, which measures the pelvis manually or by imaging to determine its adequacy for childbirth, is commonly used but not entirely reliable, according to Dr. Ami.
"A small pelvis may be able to deliver without problems, and a big pelvis might require mechanical help during childbirth," he said. "This uncertainty raises the rate of C-sections."
In the U.S., C-sections account for approximately one-third of all births. In France, the rate of mechanical problems is 30 percent, two-thirds of which are emergency procedures.
"An emergency C-section has six to seven times more morbidity and mortality than a planned C-section," Dr. Ami said. "With this virtual childbirth software, the majority of C-sections could be planned rather than emergency, and difficult instrumental extractions might disappear in the near future."
Coauthors are Lucie Cassagnes, M.D., Jean-Francois Uhl, M.D., Didier Lemery, M.D., Ph.D., Vincent Delmas, Gérard Mage, M.D., Ph.D., and Louis Boyer, M.D.
# # #
Note: Copies of RSNA 2011 news releases and electronic images will be available online at RSNA.org/press11 beginning Monday, Nov. 28.
RSNA is an association of more than 48,000 radiologists, radiation oncologists, medical physicists and related scientists committed to excellence in patient care through education and research. The Society is based in Oak Brook, Ill. (RSNA.org)
Editor's note: The data in these releases may differ from those in the printed abstract and those actually presented at the meeting, as researchers continue to update their data right up until the meeting. To ensure you are using the most up-to-date information, please call the RSNA Newsroom at 1-312-949-3233.
For patient-friendly information on MRI, visit RadiologyInfo.org.
| Abstract: |
Ami Video
- Video clip .mp4, 117 KB)
The principle of childbirth simulation. The computer evaluates the trajectory of the fetal head through the maternal pelvis.
Images (.JPG format)
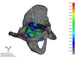
Ami Figure 1: The fetal head is considered as "fully" engaged (or "completely engaged"), when the top of the fetal head has descended through the birth canal just to the level of the maternal ischial spines, because the widest portion of the fetal head has entered the opening of the birth canal (the pelvic inlet). High-res (TIF) version (Right-click and Save As) |
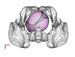
Ami Figure 2: Inferior view of the fetal head before engagement in the maternal pelvis. The rotation of the head is evaluated by describing the position of sutures and fontanels. High-res (TIF) version (Right-click and Save As) |
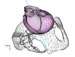
Ami Figure 3: Fetal head engaging at the pelvic inlet during childbirth simulation. The half of the maternal pelvis has been hidden for better comprehension. High-res (TIF) version (Right-click and Save As) |
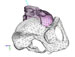
Ami Figure 4: Fetal head engaging at the pelvic inlet during childbirth simulation. The half of the maternal pelvis has been hidden for better comprehension. High-res (TIF) version (Right-click and Save As) |

 PDF
PDF